Central securities depositories
Central securities depositories Providing efficient and reliable recording and safekeeping of cash and securities
Central securities depositories ensure seamless post-trading
In post-trading, securities are actually transferred to the securities account at the client’s bank in return for payment. This task is carried out by the central securities depository (CSD).
Besides their activities in securities settlement and custody, CSDs also act as a notary on the markets; whenever a new security is issued, they keep a precise record of when a security belongs to whom and when it changes hands.
The infrastructure of the securities business
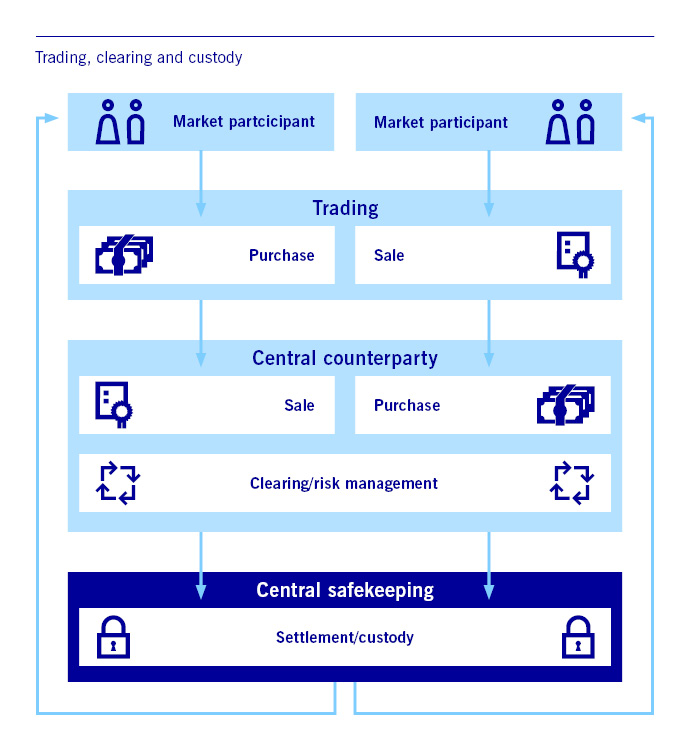
Copyright: Deutsche Börse AG
CSDs are usually the first point of contact for companies wishing to issue new securities. They also offer their clients a wide range of additional services spanning a security’s entire life cycle: from the provision of liquidity pools through to large investor networks around the globe that assist with the clients’ financing requirements.
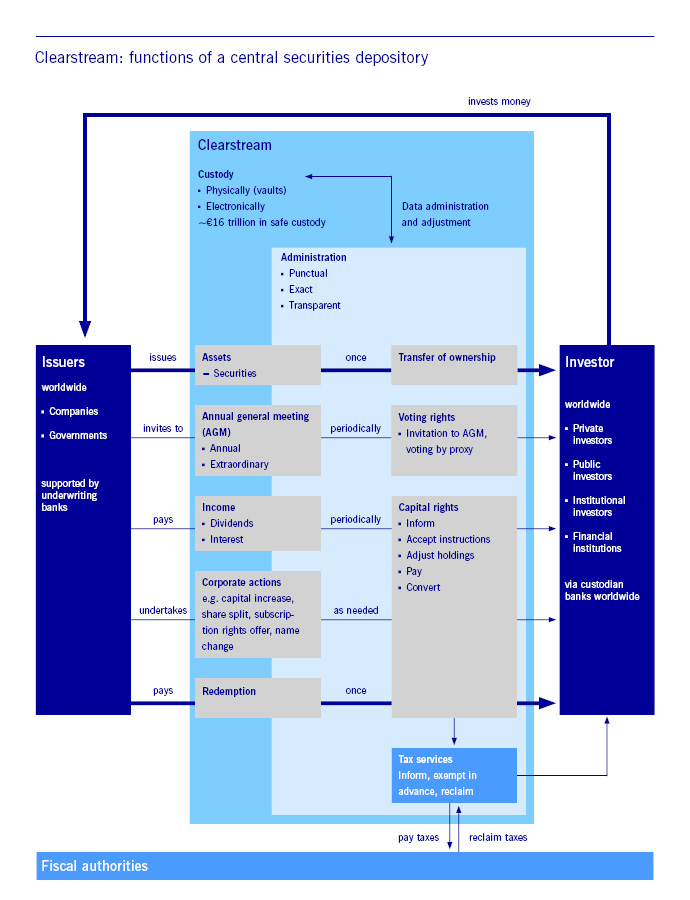
Copyright: Deutsche Börse AG
Even if it is not immediately obvious, CSDs also safeguard the transaction for small investors by ensuring that it is administered correctly and efficiently in post-trading. A typical example: a private individual buys ten Volkswagen shares from their local bank at €150 per share. Once the company shares have been purchased through the principal bank, the trade has to be settled – that is to say, cash and securities change hands. CSDs ensure precisely that.
Example 3: securities settlement for the sovereign issuing a bond
A sovereign may also decide to issue bonds, termed “sovereign bonds”. This is usually to finance the budget or to carry out a specifically government-funded project. In this case too, CSDs are important, as they assist with the sovereign bond issue by acting as a notary. Subsequently, they also offer a safe place to store the bonds and support their efficient use, for instance in collateral management.
In addition, CSDs maintain very close links with central banks. A CSD’s securities holdings may be pledged as collateral for monetary policy operations at central banks, for instance.
Harmonisation throughout the European Union
The examples show that the post-trade services provided by CSDs contribute to the stability and efficiency of capital market transactions.
At the same time, however, European post-trading and in particular the securities settlement and custody system are still decentralised, as both CSDs and banks (global custodians) operate within nationally distinct legal frameworks and on different platforms.
This has always been a serious hurdle for cross-border securities settlement and generally entails higher costs.
The European Central Bank therefore launched the TARGET2-Securities (T2S) project with the aim to create a common technical platform for securities settlement in central bank money within the European single market. In addition, the CSD Regulation created an EU-wide legal framework for CSDs. Together with T2S, this contributes to stronger harmonisation of European securities settlement systems. In future, this will lead to yet more reliability and solidity in the post-trade sector.
Clearstream, Deutsche Börse Group’s CSD, operates as a central securities depository for Germany and Luxembourg. Like other CSDs, Clearstream ensures that cash and securities change hands in the proper manner once a trade has been completed (settlement); it is also responsible for a wide range of securities services, such as issuance, asset servicing and custody.
But Clearstream’s product range does not end there: services for investment funds, for example, are gaining increasing ground. Clearstream’s fund processing platform Vestima offers direct access to local domiciled funds in 50 fund jurisdictions worldwide. In addition, its fund distribution platform Fund Centre connects distributors and fund providers across the globe. Risk and liquidity management solutions are also becoming ever more important. To enable financial institutions to handle this reliably and efficiently, Clearstream offers its clients securities financing and lending services and collateral management services. And worldwide too.
What’s more, Clearstream is one of only two international CSDs (ICSDs). Its post-trade infrastructure covers the Eurobond market and securities from 59 markets.
Deutsche Börse Group
Headquartered in Frankfurt/Main, Deutsche Börse Group is one of the largest exchange organisations worldwide. It operates markets that provide inte¬gri¬ty, transparency and security for investors wishing to invest capital and for issuers wishing to raise capital. On these markets, institutional traders buy and sell shares, derivatives and other financial instruments in accordance with clear rules and under strict supervision.
Deutsche Börse Group is now more than just a trading venue or exchange – it is a provider of financial market infrastructure. Its business areas cover the entire financial market transaction process chain. This includes the provision of indices, data and analytical solutions as well as admission, trading and clearing. Additionally, it comprises services for funds, the settlement and custody of financial instruments as well as the management of collateral and liquidity. As a technology company, the Group develops state-of-the-art IT solutions and offers IT systems all over the world.
